Joining Data Tables
| dplyr |
|---|
| 1.0.4 |
We can use dplyr’s join operations to join elements from one table to another table. Four such functions (with differing behaviors) are left_join, right_join, inner_join, and full join.
To demonstrate these functions, we’ll be joining two dataframes: df and dj.
library(dplyr)
df <- data.frame( x = c(1, 23, 4, 43, 2, 17),
y = c("a", "b", "b", "b", "a", "d"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
df x y
1 1 a
2 23 b
3 4 b
4 43 b
5 2 a
6 17 ddj <- data.frame( z = c("apple", "pear", "orange"),
y = c("a", "b", "c"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
dj z y
1 apple a
2 pear b
3 orange cIn the examples that follow, we will join both tables by the common column y.
Left join
In this example, if a join element in df does not exist in dj, NA will be assigned to column z. In other words, all elements in df will exist in the output regardless if a matching element is found in dj. Note that the output is sorted in the same order as df (the left table).
left_join(df, dj, by="y") x y z
1 1 a apple
2 23 b pear
3 4 b pear
4 43 b pear
5 2 a apple
6 17 d <NA>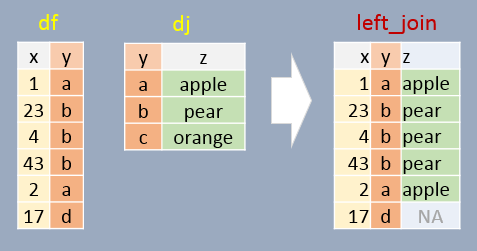
Right join
If a join element in df does not exist in dj, that element is removed from the output. A few additional important notes follow:
- All elements in
djappear at least once in the output (even if they don’t have a match indfin which case anNAvalue is added), - The output table is sorted in the order in which the
yelements appear indj. - Element
ywill appear as many times as there matchingys in `df.
right_join(df, dj, by="y") x y z
1 1 a apple
2 23 b pear
3 4 b pear
4 43 b pear
5 2 a apple
6 NA c orange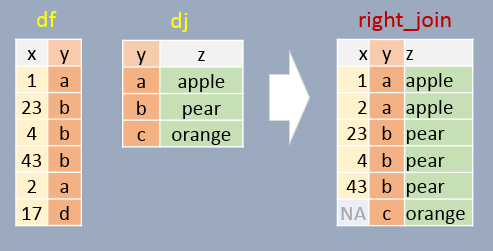
Inner join
In this example, only matching elements in both df and dj are saved in the output.
inner_join(df, dj, by="y") x y z
1 1 a apple
2 23 b pear
3 4 b pear
4 43 b pear
5 2 a apple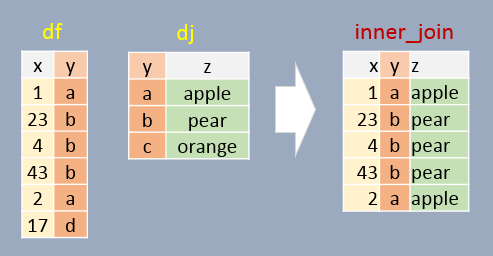
Full join
In this example, all elements in both df and dj are present in the output. For non-matching pairs, NA values are supplied.
full_join(df, dj, by="y") x y z
1 1 a apple
2 23 b pear
3 4 b pear
4 43 b pear
5 2 a apple
6 17 d <NA>
7 NA c orange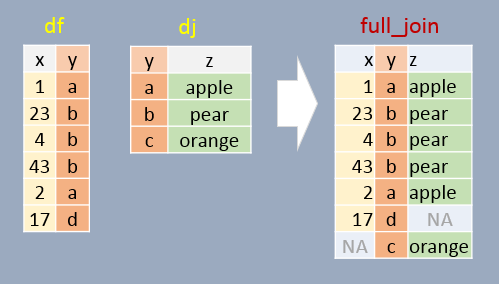
Joins in a piping operation
The afrementioned joining functions can be used with pipes. For example:
df %>%
left_join(dj, by = "y") x y z
1 1 a apple
2 23 b pear
3 4 b pear
4 43 b pear
5 2 a apple
6 17 d <NA>A note about column names
If the common columns in both tables have different names, you will need to modify the by = argument as by = c("left_col" = "right_col"). For example,
library(dplyr)
df <- data.frame( x = c(1, 23, 4, 43, 2, 17),
y1 = c("a", "b", "b", "b", "a", "d"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
dj <- data.frame( z = c("apple", "pear", "orange"),
y2 = c("a", "b", "c"),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
left_join(df, dj, by = c("y1" = "y2")) x y1 z
1 1 a apple
2 23 b pear
3 4 b pear
4 43 b pear
5 2 a apple
6 17 d <NA>